
Research Unveils Tidal Forces as Key Factor in Antarctic Iceberg Calving
Alright, so scientists have been scratching their heads about how these massive icebergs break off from Antarctica's ice shelves. Turns out, it might be simpler than we thought. A new study points to tidal forces, especially during springtime when they're at their peak, as a major factor in these calving events. It's kind of like how the moon pulls the tides on our oceans, but on a much grander, icier scale.
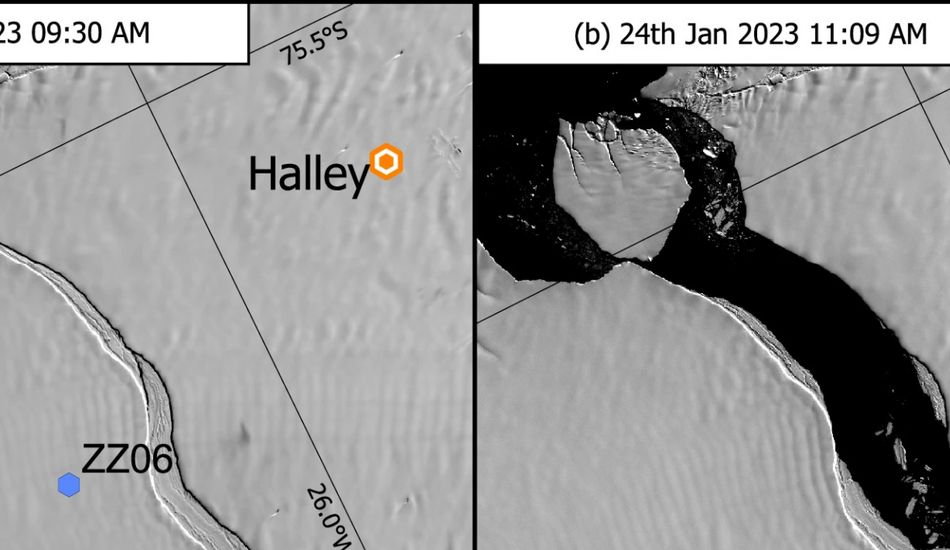
Researchers focused on the Brunt Ice Shelf, where a colossal iceberg, almost twice the size of New York City, broke off back in 2021. They created a mathematical model to simulate the forces acting on the ice shelf, factoring in things like ocean tides and wind patterns. And guess what? The model showed that the cracks in the ice tended to grow the most during springtime, when the tides are strongest. Pretty neat, huh?
Oliver Marsh, the lead author of the study, mentioned that understanding the timing of these calving events is super important. It's not just about the shape of the ice shelf; it also affects its long-term stability. Plus, these icebergs can influence ocean circulation and local ecosystems, so it's a big deal all around.
However, it's not all sunshine and icebergs. The model is a simplified version of what's actually happening in Antarctica. Things like climate change and extreme temperatures can cause even bigger rifts in the ice. One thing that the study shows is that the model is important and it can improve prediction models for calving events, a historically challenging task.
Even with its limitations, this study is a step in the right direction. It helps us better understand the role of environmental factors in iceberg calving. And that knowledge could be used to improve our models for predicting how icebergs will behave under extreme conditions. Which, let's be honest, is pretty crucial in a world that's getting warmer.
Think of it this way: It's like understanding the foundation of a house before a storm hits. The better we understand the forces at play, the better we can predict and prepare for the future. It can also help us better comprehend changes in the sea level with greater precision.
1 Image of Iceberg Formation:

Source: Gizmodo